Step 1 : aodv.h
Please search for aodv.h header file under AODV folder in NS-2 directory.
Open it and search for rt_down( ) function
Open it and search for rt_down( ) function
void
rt_down(aodv_rt_entry *rt);
void routeTablePrint(nsaddr_t routeNode_id); // Method added after rt_down();
Step 2: aodv.cc
Open the aodv.cc file and search for rt_down function to add
routeTablePrint() function below to it.
void AODV::rt_down(aodv_rt_entry *rt)
void AODV:: routeTablePrint(nsaddr_t routeNode_id)
{
FILE * routeFile;
char routeFileName[50] = "AodvRoutingTable.txt"; //You can give your desired name
routeFile= fopen(routeFileName, 'a');
aodv_rt_entry *rt;
fprintf(routeFile, "**************************************************");
for (rt=rtable.head();rt; rt = rt->rt_link.le_next) {
fprintf(routeFile, "NODE: %it %.4lft %it %it %it %it %it %.4lft %d n", node_id, CURRENT_TIME, rt->rt_dst, rt->rt_nexthop, rt->rt_hops, rt->rt_seqno, rt->rt_expire, rt->rt_flags)
}
fclose(routeFile);
} //end of routeTablePrint
FILE * routeFile;
char routeFileName[50] = "AodvRoutingTable.txt"; //You can give your desired name
routeFile= fopen(routeFileName, 'a');
aodv_rt_entry *rt;
fprintf(routeFile, "**************************************************");
for (rt=rtable.head();rt; rt = rt->rt_link.le_next) {
fprintf(routeFile, "NODE: %it %.4lft %it %it %it %it %it %.4lft %d n", node_id, CURRENT_TIME, rt->rt_dst, rt->rt_nexthop, rt->rt_hops, rt->rt_seqno, rt->rt_expire, rt->rt_flags)
}
fclose(routeFile);
} //end of routeTablePrint
Step 3: Usage
The routeTablePrint() function in generic and can be used where ever you want to print the routing information in AODV. For an instance, It can be used while route request generated node receives route reply message (RREP).
if (ih->daddr() == index) {
routeTablePrint(index); // print routing table
rt->rt_disc_latency[(unsigned char)rt->hist_indx] = (CURRENT_TIME - rp->rp_timestamp)
/ (double) rp->rp_hop_count;
// increment indx for next time
rt->hist_indx = (rt->hist_indx + 1) % MAX_HISTORY;
}
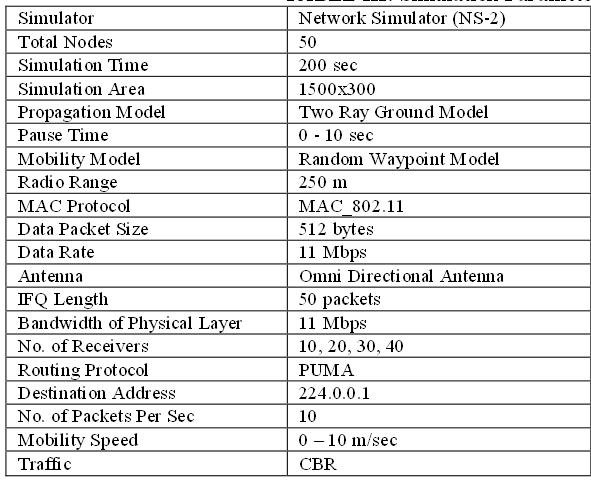
The same procedure will be followed for any routing protocol like AODV,DSR,PUMA etc.. .